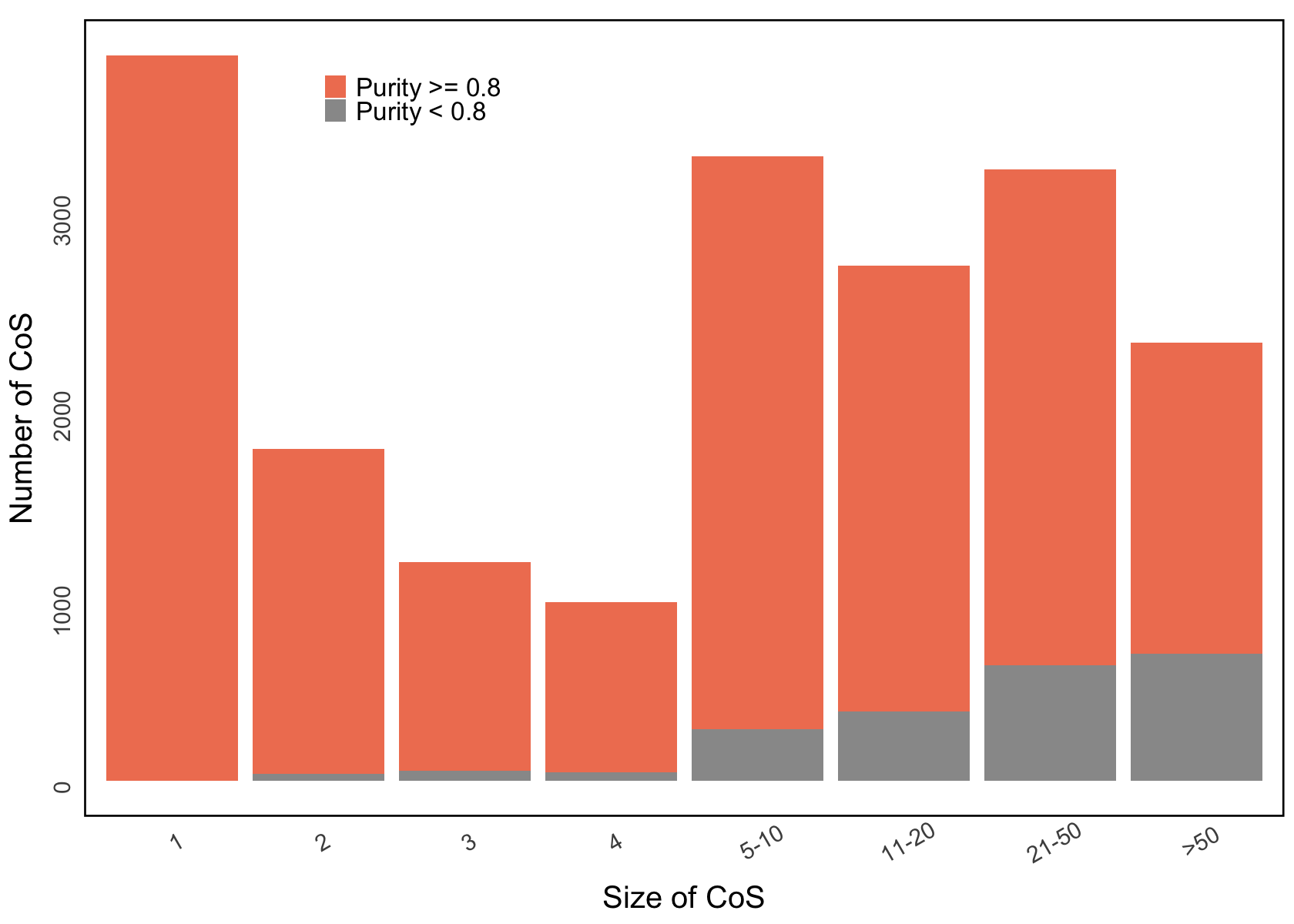
Figure 3g. Empirical distribution of the number of 95% CoS versus the size of the CoS.#
Empirical distribution of the number of 95% CoS in terms of the number of variants each CoS contained. CoS are color-coded by purity, with high-purity sets (purity > 0.8) distinguished from moderate-purity sets (0.5 < purity ≤ 0.8).
library(tidyverse)
library(ggpattern)
library(ggpubr)
library(cowplot)
res <- readRDS("data/xQTL_only_colocalization.rds")
── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──────────────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.5
✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
✔ ggplot2 3.5.1 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
✔ lubridate 1.9.4 ✔ tidyr 1.3.1
✔ purrr 1.0.4
── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors
Attaching package: ‘cowplot’
The following object is masked from ‘package:ggpubr’:
get_legend
The following object is masked from ‘package:lubridate’:
stamp
Organize input data#
sets_variants <- lapply(res$colocalized_variants, function(cv){ unlist(strsplit(cv, "; ")) })
sets_vcp <- lapply(res$colocalized_variants_VCP, function(cv){ unlist(strsplit(cv, "; ")) })
sets_num_variants <- sapply(sets_variants, length)
sets_purity <- as.numeric(res$purity)
variants_number <- table(sets_num_variants)
data <- data.frame(variants_number = as.numeric(variants_number),
categories = as.numeric(names(variants_number)))
data$proportion <- data$variants_number / sum(data$variants_number)
purity <- c()
for (i in 1:nrow(data)){
num <- data$categories[i]
pos <- which(sets_num_variants == num)
purity_cate <- sets_purity[pos]
purity <- c(purity, c(sum(purity_cate>=0.8), sum(purity_cate<0.8)))
}
data.purity <- data.frame(
number = rep(data$variants_number, each=2),
categories = rep(data$categories, each = 2),
purity = purity,
if_pure = rep(c("Purity >= 0.8", "Purity < 0.8"), times = nrow(data))
)
new_data <- data.purity %>%
mutate(group = case_when(
categories == 1 ~ "1",
categories == 2 ~ "2",
categories == 3 ~ "3",
categories == 4 ~ "4",
categories %in% 5:10 ~ "5-10",
categories %in% 11:20 ~ "11-20",
categories %in% 21:50 ~ "21-50",
categories >= 50 ~ ">50"
)) %>%
group_by(group, if_pure) %>%
summarise(
variants_number = sum(purity),
) %>%
ungroup() %>%
mutate(proportion = variants_number / sum(variants_number)) %>%
mutate(group = factor(group, levels = c("1", "2", "3", "4", "5-10", "11-20", "21-50", ">50")))
new_data$if_pure <- factor(new_data$if_pure, levels = c("Purity >= 0.8", "Purity < 0.8"))
overall_proportions <- new_data %>%
group_by(group) %>%
summarise(overall_proportion = sum(proportion),
max_variants_number = sum(variants_number)) %>%
ungroup()
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'group'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Distribution plot#
library(ggplot2)
p1 <- ggplot(new_data, aes(x = group, y = variants_number, fill = if_pure)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "stack") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Purity < 0.8" = "grey60", "Purity >= 0.8" = "#F08060")) +
labs(
title = "",
x = "Size of CoS",
y = "Number of CoS",
fill = ""
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 15) + # Use a minimal theme with a larger base font size
theme(
plot.title = element_text( size = 0 ),
axis.title.x = element_text( margin = margin(t = 0), size = 24), # Adjust x axis title margin
axis.title.y = element_text(margin = margin(r = 10), size = 24), # Adjust y axis title margin
axis.text.x = element_text(margin = margin(t = 10), size = 18, angle = 30), # Adjust x axis text margin
axis.text.y = element_text(margin = margin(r = 5), size = 18, angle = 90), # Adjust y axis text margin
legend.position = "inside",
legend.justification = c(0.23, 0.95),
legend.title = element_text(size = 0),
legend.text = element_text(size = 20),
panel.grid.major = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
panel.border = element_rect(color = "black", fill = NA, linewidth = 1.5)
)