Simulating Cis-QTL Data
Alex McCreight
2025-12-17
Source:vignettes/cis_qtl_simulation.Rmd
cis_qtl_simulation.RmdThis vignette demonstrates how to use the
generate_cis_qtl_data() function to simulate cis-eQTL data
with a multi-component genetic architecture:
- Sparse effects: Few SNPs with large effects
- Oligogenic effects: Moderate number of SNPs with medium effects
- Infinitesimal/polygenic effects: Many SNPs with small effects
Example 1: Fixed Number of Non-zero SNPs
In this example, we specify a fixed number of SNPs for each component
(n_sparse = 2, n_oligogenic = 5,
n_inf = 15):
result1 <- generate_cis_qtl_data(
G = G,
h2g = 0.25,
prop_h2_sparse = 0.50,
prop_h2_oligogenic = 0.35,
prop_h2_infinitesimal = 0.15,
n_sparse = 2,
n_oligogenic = 5,
n_inf = 15,
independent = TRUE,
max_attempts = 200
)
# Number of causal SNPs in each component
cat("Sparse SNPs:", length(result1$sparse_indices), "\n")
# Sparse SNPs: 2
cat("Oligogenic SNPs:", length(result1$oligogenic_indices), "\n")
# Oligogenic SNPs: 5
cat("Infinitesimal SNPs:", length(result1$infinitesimal_indices), "\n")
# Infinitesimal SNPs: 15
plot(abs(result1$beta), ylab = "Absolute Effect Size", xlab = "SNP Index", pch = 16)
points(which(result1$beta != 0), abs(result1$beta[result1$beta != 0]), col = 2, pch = 16)
Example 2: Infinitesimal Background
Setting n_inf = NULL assigns infinitesimal effects to
all remaining SNPs after sparse and oligogenic selection, creating a
polygenic background:
result2 <- generate_cis_qtl_data(
G = G,
h2g = 0.25,
prop_h2_sparse = 0.50,
prop_h2_oligogenic = 0.35,
prop_h2_infinitesimal = 0.15,
n_sparse = 2,
n_oligogenic = 5,
n_inf = NULL,
independent = TRUE,
max_attempts = 200
)
# Number of causal SNPs in each component
cat("Sparse SNPs:", length(result2$sparse_indices), "\n")
# Sparse SNPs: 2
cat("Oligogenic SNPs:", length(result2$oligogenic_indices), "\n")
# Oligogenic SNPs: 5
cat("Infinitesimal SNPs:", length(result2$infinitesimal_indices), "\n")
# Infinitesimal SNPs: 4993
plot(abs(result2$beta), ylab = "Absolute Effect Size", xlab = "SNP Index", pch = 16)
causal_idx <- c(result2$sparse_indices, result2$oligogenic_indices)
points(causal_idx, abs(result2$beta[causal_idx]), col = 2, pch = 16)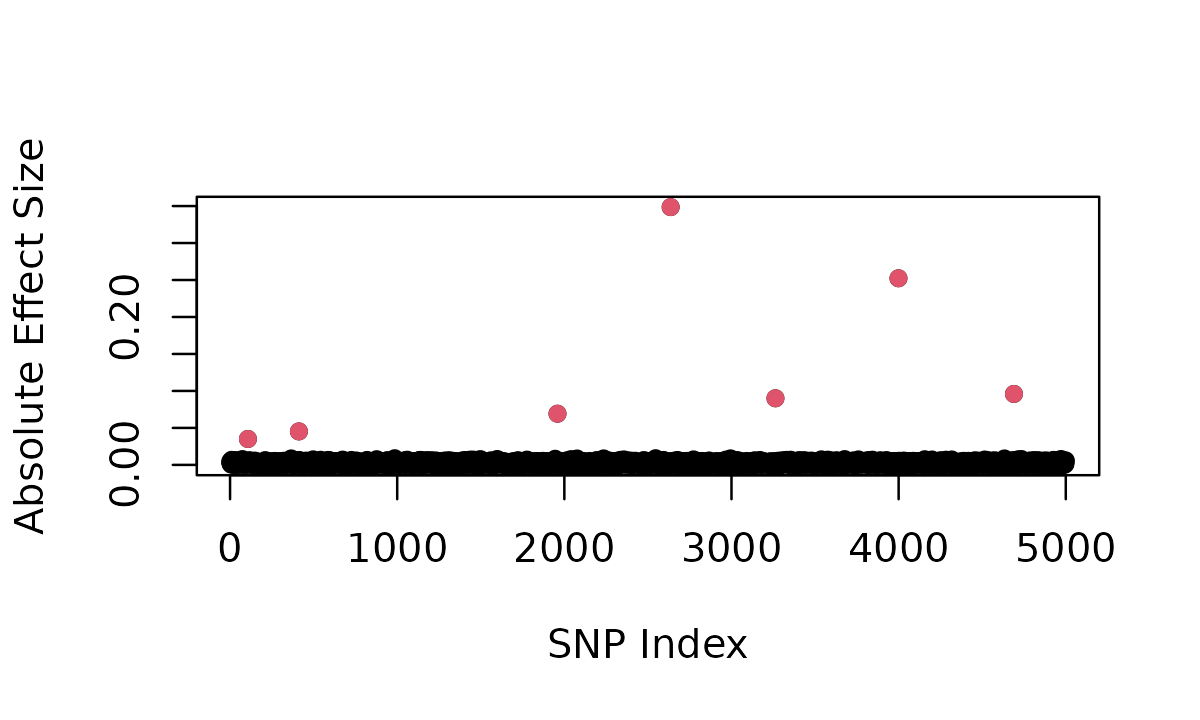
Key Parameters
-
h2g: Total heritability (default 0.25) -
prop_h2_sparse,prop_h2_oligogenic,prop_h2_infinitesimal: Proportion of heritability explained by each component (must sum to 1) -
n_sparse: Number of sparse (large effect) SNPs -
n_oligogenic: Number of oligogenic (medium effect) SNPs -
n_inf: Number of infinitesimal/polygenic SNPs. IfNULL, all remaining SNPs receive infinitesimal effects -
independent: IfTRUE, sparse and oligogenic SNPs are constrained to have low LD (|r| < 0.15)
Output Structure
The function returns a list with all simulation components:
names(result1)
# [1] "G" "y" "beta"
# [4] "h2g" "h2_sparse" "h2_oligogenic"
# [7] "h2_infinitesimal" "sparse_indices" "oligogenic_indices"
# [10] "infinitesimal_indices" "residual_variance" "causal"Verify LD Constraint
When independent = TRUE, sparse and oligogenic SNPs
should have low LD with each other:
# Check LD among sparse SNPs
if (length(result1$sparse_indices) > 1) {
sparse_cor <- cor(G[, result1$sparse_indices])
cat("Max |r| among sparse SNPs:", round(max(abs(sparse_cor[upper.tri(sparse_cor)])), 3), "\n")
}
# Max |r| among sparse SNPs: 0.023
# Check LD among oligogenic SNPs
if (length(result1$oligogenic_indices) > 1) {
oligo_cor <- cor(G[, result1$oligogenic_indices])
cat("Max |r| among oligogenic SNPs:", round(max(abs(oligo_cor[upper.tri(oligo_cor)])), 3), "\n")
}
# Max |r| among oligogenic SNPs: 0.062
# Check LD between sparse and oligogenic SNPs
cross_cor <- cor(G[, result1$sparse_indices, drop = FALSE],
G[, result1$oligogenic_indices, drop = FALSE])
cat("Max |r| between sparse and oligogenic:", round(max(abs(cross_cor)), 3), "\n")
# Max |r| between sparse and oligogenic: 0.05